Recognizing Gum Infection Symptoms: A Global Perspective
Introduction
Gum infections, also known as periodontal disease, can be a silent threat to your oral health. Understanding the symptoms and seeking timely treatment is crucial for preventing long-term damage. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the common symptoms of gum infections and provide global statistics to highlight the prevalence of this dental condition.
Gum Infection Symptoms: What to Look For
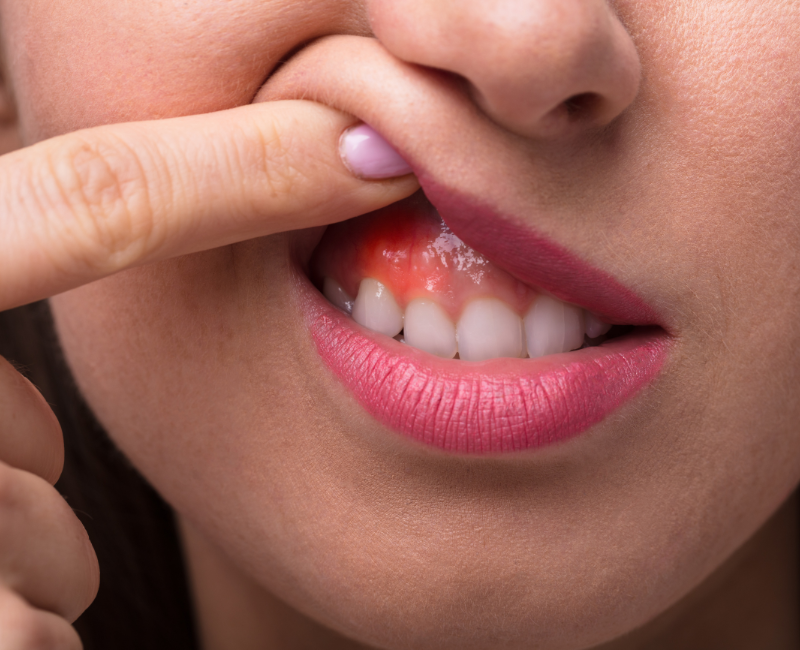
- Gum Bleeding: One of the earliest signs of gum infection is bleeding when brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed during regular oral hygiene routines.
- Swollen or Red Gums: Inflammation and discoloration of the gums can indicate an underlying infection. Healthy gums should appear pink and firm.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Also known as halitosis, chronic bad breath is often a sign of bacterial activity associated with gum infections.
- Receding Gums: As the infection progresses, gums may start to recede, exposing more of the tooth’s surface. This can lead to tooth sensitivity.
- Loose Teeth or Changes in Bite: Advanced gum infections can weaken the supporting structures of teeth, leading to mobility or changes in how your teeth fit together.
- Pus Formation: In severe cases, pus may develop around the gumline, indicating an active infection that requires immediate attention.
Global Statistics on Gum Infections
Recent data compiled by the World Dental Federation (FDI) reveals the widespread nature of gum infections:
- Approximately 20-50% of the global population suffers from some form of gum disease.
- In high-income countries, prevalence rates range from 5-15%, while in low-income countries, the rates can exceed 50%.
Preventing Gum Infections: Tips for Oral Health
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental visits are crucial for early detection and prevention of gum infections.
- Effective Oral Hygiene Practices: Brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help maintain healthy gums.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in nutrients, particularly vitamins C and D, can support gum health.
- Avoid Smoking and Tobacco Products: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, including gum disease.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports saliva production, which helps to cleanse the mouth of harmful bacteria.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of gum infections and taking proactive steps towards oral health is essential for overall well-being. Global statistics highlight the widespread nature of this condition, underscoring the importance of regular dental care and maintenance.
If you suspect you may have gum infection symptoms, don’t delay seeking professional dental care. Early intervention can prevent further damage and help you maintain a healthy, confident smile for years to come. Remember, your oral health is an integral part of your overall health and should be prioritized accordingly.