From Healthy to Hurting: The Stages of Tooth Decay Explained
We all know the importance of brushing and flossing, but have you ever wondered what exactly is happening inside your mouth if you don’t? It’s a journey from a healthy tooth to a painful problem, and it’s a process known as tooth decay. Understanding the stages of tooth decay is the first step toward prevention and timely treatment.
Tooth decay, or dental caries, is a common chronic disease caused by bacteria in your mouth. These bacteria feed on sugars from the foods and drinks you consume, producing acids that erode your tooth enamel. Let’s break down this gradual process into its key stages.
Stage 1: Demineralization
This is the earliest and most reversible stage. It’s not a cavity yet, but a warning sign. The acids produced by bacteria begin to strip away minerals like calcium and phosphate from your tooth’s protective outer layer, the enamel. This process is called demineralization. At this point, you might see a chalky white or brown spot on the tooth surface. The good news? This is your window of opportunity! With excellent oral hygiene, a fluoride treatment from your dentist, and a healthy diet, you can often reverse this stage and remineralize the enamel, preventing a full-blown cavity from forming.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
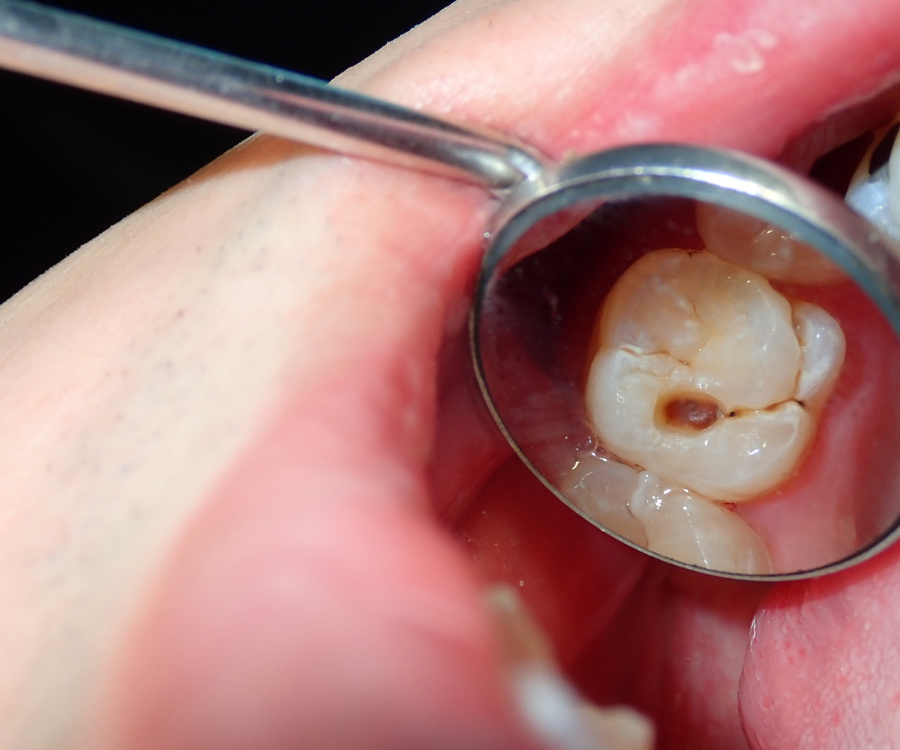
If the demineralization isn’t addressed, the enamel continues to weaken. Eventually, a small hole or cavity will form. This is the first true cavity, and it’s a sign that the erosion has become permanent. At this stage, you might not feel any pain, as the enamel has no nerves. This is why regular dental check-ups are so crucial; your dentist can spot and treat these small cavities with a simple filling, stopping the decay in its tracks.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
Beneath the enamel lies the dentin, a softer, yellowish layer of the tooth. Dentin is much more sensitive than enamel because it’s connected to the tooth’s nerves. Once the decay breaks through the enamel and reaches the dentin, the process accelerates. You may start to feel a twinge of sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks. The cavity will also grow much faster at this stage. A filling is still the most common treatment, but the size and depth of the cavity will determine the type of restoration needed.
Stage 4: Pulp Involvement
The pulp is the innermost part of the tooth, a chamber filled with blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. When the decay reaches this stage, it’s a serious problem. The bacteria cause an infection in the pulp, leading to inflammation and often intense pain. This is the throbbing toothache that most people associate with a serious dental problem. At this point, a simple filling won’t be enough. Your dentist will likely recommend a root canal, a procedure to remove the infected pulp and save the tooth.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation
If the infection in the pulp isn’t treated, it can spread beyond the tooth’s root tip and into the surrounding bone and gum tissue. This leads to the formation of a pocket of pus called a dental abscess. An abscess can be extremely painful and cause facial swelling, fever, and a general feeling of being unwell. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention from a dentist or endodontist. Treatment typically involves draining the abscess, a root canal, or, in severe cases, tooth extraction.
Stage 6: Tooth Loss
This is the final, unfortunate stage of untreated tooth decay. The tooth becomes so compromised by the infection and decay that it cannot be saved. The only remaining option is to extract it. Losing a tooth can have significant consequences for your bite, the alignment of your other teeth, and your overall oral health.
The progression of tooth decay can be a slow process, but it is relentless. Knowing the stages of tooth decay highlights the importance of proactive dental care. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and a consistent oral hygiene routine are your best defense against this common but preventable disease. Don’t wait for the pain to begin – see your dentist to keep your smile healthy and happy for life.